Using these CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14- Statistics Objective Questions with solutions as reference material will help the students to score good marks. Students can get here the objective questions chapter wise, which have also been organized topic-wise in the PDF. Chapter 14-Statistics deals with a branch of Mathematics that includes the representation of data in a meaningful way. From this chapter, students can learn the step deviation methods, finding mode and median of grouped data, converting frequency distribution and the relation between, mode, mean and median methods, and so on. CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14- Statistics Objective Questions is a good resource to prepare for the exams.
Sub-Topics From Chapter 14 Statistics
These CBSE Class 10 Maths objective questions from this chapter 14 have been organized topic wise and students referring to these will be able to score good marks in the exam. The topics discussed are given as follows:
14.1 Introduction to Statistics (3 MCQs From The Given Topic)
14.2 Graphical representation of cumulative frequency distribution
14.3 Mean (7 MCQs From This Topic)
14.4 Median (1 MCQs Listed From Topic)
14.5 Mode (4 MCQs From This Given Topic)
14.6 Ogives and Questions relating to the relation between mean, mode and median (2 MCQs From Topic)
Download CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14- Statistics Objective Questions Free PDF
Introduction to Statistics
1. Class mark of a class is obtained by using
a. (upper limit – lower limit) / 2
b. (upper limit + lower limit) / 2
c. upper limit – lower limit
d. Upper limit + lower limit
Answer: (b) (upper limit + lower limit) / 2
Solution: Class mark is the midpoint of a class interval. Therefore, its formula is given by (upper limit + lower limit) / 2
2. Look at the following table below.
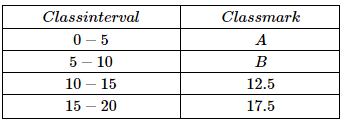
The value of A & B respectively are:
a. 3,8
b. 2,7
c. 3,7
d. 2.5, 7.5
Answer: (d) 2.5, 7.5
Solution: Class mark for a class interval = (Upper-class limit + Lower-class limit)/ 2
For first class upper class limit is 5 and lower is 0. Thus class mark for it is 2.5 using formula.
For 2nd class upper class limit is 10 and lower limit is 5. Thus class mark for it is 7.5.
3. If the sum of all the frequencies is 24, then the value of z is:

a. 4
b. 6
c. 8
d. 10
Answer: (d) 10
Solution: Here, n=∑fi=z+5+6+1+2=14+z
Given: ∑fi=24
∴n=∑fi=14+z=24
⇒z=24−14=10.
4. The value of ∑ni=1xi is

Mean
5. The mean of the following distribution is

6.

a. 208
b. 444
c. 88
d. 40
Answer: (b) 444
Solution: Each term on right most column is the product of corresponding 2 terms on 1st 2 columns. 1st column is class marks list. 2nd column is frequencies for these columns. The 3rd column is the product of these 2 columns.
For first row, class mark (xi) = 4, frequency (fi) = 10. Product (fixi) = 40. Similarly the products of other class marks can also be found.
The sum of these products (∑fixi) = 40 + 88 + 108 + 208 = 444
7. Consider the following distribution of SO2 concentration in the air (in ppm = parts per million) in 30 localities. Find the mean SO2 concentration using assumed mean method. Also find the values of A, B and C.

a. -0.04, 0, 0.04, 0.5
b. -0.04, 0, 0.04, 0.6
c. -0.04, 0, 0.04, 0.2
d. -0.04, 0, 0.04, 0.098
Answer: (d) -0.04, 0, 0.04, 0.098
Solution: The 4th column in table shown in question is a table of values of‘d’.
di = xi – a
Here
di = value of‘d’ for ith class mark-row.
xi = ith class mark
a = assumed mean value
Applying given formula for 1st class interval (0-0.04),
-0.08 = 0.02 – a
a = 0.1
Thus P = 0.1
Applying given formula for 2nd class interval (0.04-0.08)
A = 0.06 – 0.1
A = -0.04
Similarly for 3rdand 5th classes d values are-
B = 0
C = 0.04
Mean = 0.098
8. There is a grouped data distribution for which mean is to be found by step deviation method.

Find the value of A, B, C, D, E and F respectively.
a. 186 , -100, -200, -2 ,-1 and 2
b. 188 , -100, 200, -2 ,-1 and 2
c. 188 , 100, -200, 2 ,-1 and -2
d. 186 , 100, -200, -2 ,-1 and 2
Answer: (b) 188, -100, 200, -2,-1 and 2
Solution: ∑fi = sum of frequencies of each class = 40 + 39 + 34 + 30 + 45 = 188
di = xi – a
where xi = ith class mark
a = assumed mean
Using above formula for 1st class (0-100) we get-
-200 = 50 – a
a = 250
Using above formula for 2nd class (100-200) we get-
B = 150 – 250
B = -100
Similarly, C = 200.
ui = (di)/ h
Here h = class interval = 100. h is constant.
For 1st class (0-100),
ui = (di)/ h= – (200/100) =-2
Thus, D = -2
Similarly E = -1, F = 2
A, B, C, D, E and F are 188, -100, 200, -2,-1 and 2 respectively.
9. The formula for finding mean by direct method is
 Where B and A are respectively
Where B and A are respectively
(A) Class mark, frequency of the class
(B) Average frequency, class size
(C) Class size, average frequency
(D) Frequency of the class, class mark
Answer: (A) Class mark, frequency of the class
Solution:

Where B is the class mark.
Class mark = 1/2 (upper limit of class + lower limit of class)
And A is the frequency of the class.
10. The average weight of a group of 25 men was calculated to be 78.4 kg. It was discovered later that one weight was wrongly entered as 69 kg instead of 96 kg. What is the correct average ?
(A) 75.76
(B) 77.56
(C) 79.48
(B) 80.30
Answer: (C) 79.48
Solution: Total weight of 25 men = 25 × 78.4 = 1960
Due to the error in one entry, 96 has become 69
Difference= 27 kg
∴ Correct total = 1960 + 27 = 1987
∴ Correct total =1987 / 25=79.48
Median
11. (For an arranged data) The median is the
(A) Most common observation
(B) Middle most observation
(C) Least common observation
(D) Average of the two most common observations
Answer: (B) Middle most observation
Solution: The median is the middle most observation. If there is even number of observations, median is the average of the two middle observations. If there is odd number of observations, median is the middle observation itself.
Mode
12. The mode of the following data is:

(A) 16
(B) 14
(C) 12
(D) 10
Answer: (B) 14
Solution: The mode is the most frequent observation. Here, the mode is 14 with a frequency of 15.
13. Find the mode of the following data.

- Between 20 and 22.5
- Between 27.5 and 30
- Equal to 25
- Between 22.5 and 27.5 but not equal to 25
Answer: (A) Between 20 and 22.5
Solution:

Modal Class is 20-30
Mode= l +

= 20 + (14-13) / (28-13-5) × 10 =21
Hence, the mode will be between 20 and 22.5
14. There are lottery tickets labelled numbers from 1 to 500. I want to find the number which is most common in the lottery tickets. What quantity do I need to use?
(A) None of the above
(B) Mode
(C) Mean
(D) Median
Answer: (B) Mode
Solution: In a distribution, mode gives the data whose frequency is highest. This means that for an ungrouped distribution the mode is the value of the data that repeats maximum number of times. For the lottery tickets I want to find the most repeated number. Mode will serve this purpose.
15. Which of the following is not a measure of central tendency?
(A) Mode
(B) Range
(C) Median
(D) Mean
Answer: (B) Range
Solution: Three measures of central tendency are mean, median, mode. Range is a measure of variability or spread of the data.
Ogives and Questions relating to the relation between mean, mode and median
16. The mode of a frequency distribution can be determined graphically from:
(A) Frequency curve
(B) 0give
(C) Frequency polygon
(D) Histogram
Answer: (B) Ogive
Solution: The mode of a frequency distribution can be determined graphically from ogive
17. For ‘more than ogive’ the x-axis represents:
(A) frequency
(B) lower limits of class intervals
(C) mid-values of class-intervals
(D) upper limits of class-intervals
Answer: (B) lower limits of class intervals
Solution: For ‘more than ogive’ the x-axis represents lower limits of class intervals
From the compilation of objective questions of chapter 14, students can find the methods and procedure to solve these sums. These have been explained in a broad way in these MCQs with solutions, such that students understand the fundamentals, quickly and easily.
These extra questions from CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 is given here for the students to solve and practice.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Extra Questions
1. Given that the mean of first n natural numbers is 5n/9, then calculate “n”.
(a) 9
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 10
2. If 35 is removed from the data, 30, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, then how much does the median increase by?
(a) 1
(b) 0.5
(c) 2
(d) 1.5
Stay tuned for further updates on CBSE Study Material. To access interactive Maths and Science Videos download BYJU’S App and subscribe to YouTube Channel.


